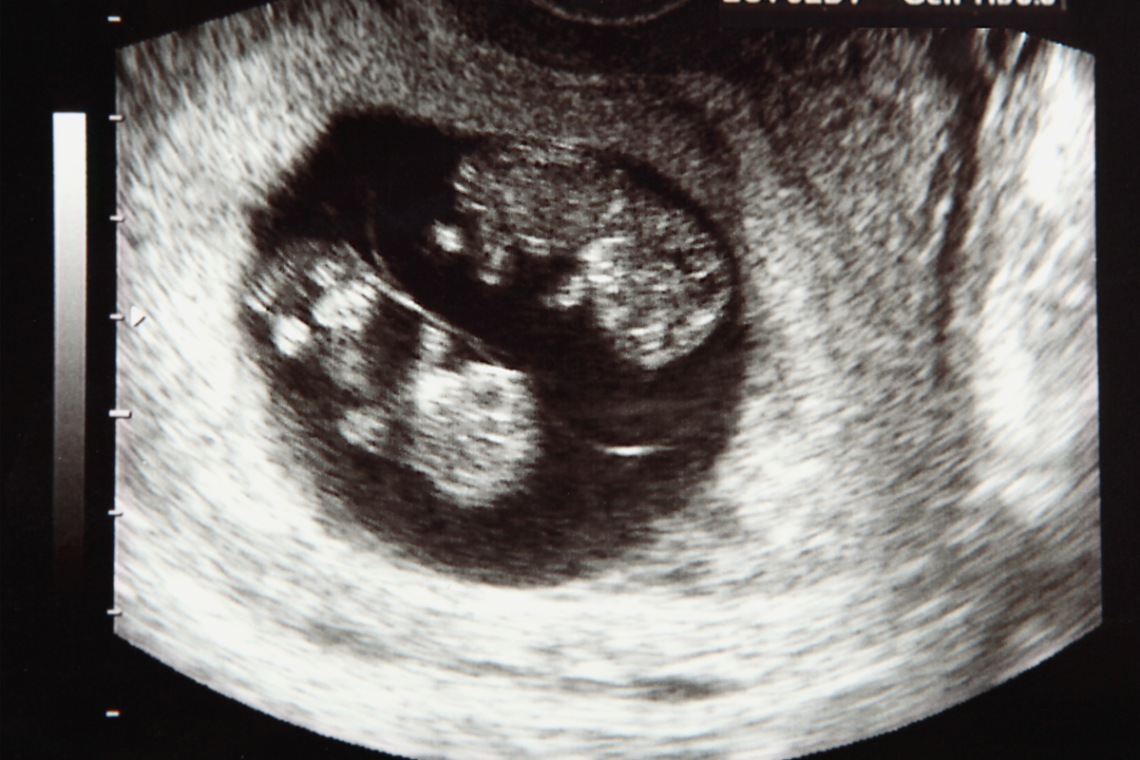
Ever heard someone ask, “Do twins run in your family?” or even, “Are they identical?” when referring to a set of boy/girl twins (gasp!)? These curious bystanders at the store mean well, but they are probably just asking the same ol’ twin questions they ask everyone. Where the most common types of twins are identical (monozygotic) and fraternal (dizygotic), did you know there are actually a handful of other rare types? Twins are fascinating and unique, and there are several types of twins that you might not be aware of. So let’s dive in and explore different types of twins.
What Exactly Defines Twins?
Twins are individuals who are born from the same pregnancy and share the same genetic material. Identical twins are genetically identical and develop from a single fertilized egg that splits into two identical embryos. Fraternal twins, on the other hand, develop from two separate eggs that are fertilized by two different sperm cells and are no more genetically similar than any other siblings.
What are the more common types of twins?
What are Identical Twins?
Identical twins, also known as monozygotic twins, are siblings who originate from a single fertilized egg. Identical twins are formed when a single fertilized egg splits into two embryos during the early stages of pregnancy. This process occurs randomly and is not influenced by any external factors. Once the egg has split, each embryo develops independently and has its own placenta and amniotic sac. This means that identical twins are not always identical in every way, as some differences may arise due to variations in the environment in which each embryo develops.
Identical twins share the same genetic material and are essentially clones of each other. In most cases, identical twins are 99% always the same sex. On rare occasions, they can be a different sex that has resulted in a genetic mutation. Identical twins have several similarities in terms of physical features, such as hair and eye color, height, and weight. They also tend to have similar personalities, preferences, and behavior patterns.

Common Misconceptions: There are several misconceptions about identical twins, one of which is that they always look exactly the same. While they share the same genetic material, they may have subtle physical differences due to factors like environmental influences. Another misconception is that identical twins have a telepathic connection or can read each other’s thoughts. While they may have a close bond and be able to anticipate each other’s actions, this is not due to any supernatural ability. Finally, some people believe that identical twins have identical personalities, but this is not always the case. While they may share some traits and tendencies, they are still individuals with their own unique experiences and perspectives.
What Are Fraternal Twins?
Fraternal twins are siblings that are born at the same time but come from two separate fertilized eggs. They are also known as dizygotic twins. Fraternal twins occur when two eggs are released during ovulation and are fertilized by two separate sperm. Fraternal twins can run in families, but there is also an increased chance of having fraternal twins if a woman is over the age of 35 or has undergone fertility treatments.
Fraternal twins are not more alike than any other siblings, and they can be of different sexes or have different physical characteristics, such as hair and eye color.

Differences between fraternal and identical twins:
Fraternal and identical twins differ in how they are formed and in their genetic makeup. It’s all about the DNA. Simply put, identical twins share the same DNA, fraternal twins don’t.
What are the more rare types of twins?
What are Mirror Image Twins?
Mirror image twins are a type of identical twins that share the same genetic material. Mirror image twins are formed when a fertilized egg splits into two identical cells, which then develop into two separate embryos. The key thing to remember here is that the split occurs after the ninth day of conception, when the developing embryos have already started to differentiate. This delayed splitting can result in the reversal of some physical traits, leading to mirror-image twins.
Mirror image twins have unique features such as opposite hair whorls and birthmarks on opposite sides of their bodies. They can even share the same facial features and body build.
What Are Conjoined Twins?
Conjoined twins are identical twins who are physically connected to each other at some point in their bodies. They are formed when a single fertilized egg fails to separate completely during the early stages of pregnancy. As a result, the developing fetus divides incompletely and the two embryos remain joined together.
Conjoined twins are extremely rare, occurring in only 1 in 50,000 live pregnancies. Conjoined twins share the same DNA and often have similar physical features. They can have different personalities and interests. The degree of connection between the twins can range from a small piece of skin that bridges them together to a complex fusion of organs and limbs.
Types of Conjoined Twins
The type of conjoined twins depends on the stage of embryonic development at which the separation process was interrupted. The most common type is thoracic-omphalopagus. This is where the twins are joined at the chest and abdomen. This means they may share a liver, gastrointestinal tract, and possibly other organs. Other types include cephalopagus, in which the twins are joined at the head, and pygopagus, in which the twins are joined at the lower back or buttocks.
What are Superfecundation Twins?
Superfecundation twins are a rare occurrence. This occurs when a woman releases two eggs during ovulation. These two eggs are fertilized by two different sperm from separate sexual partners within the same ovulation cycle. This results in twins who have different biological fathers and are therefore not genetically identical. The occurrence of superfecundation twins is extremely rare and only accounts for 2% of all twin births.
Superfecundation twins are formed when a woman has sexual intercourse with two separate partners within the same ovulation cycle. The first sperm fertilizes one egg, and the second sperm fertilizes the other egg. The two embryos then develop independently of each other and are born as twins. The time between the two acts of sexual intercourse can vary. It is believed, however, that it must occur within 24-48 hours of each other for the woman to release two eggs.
What are Semi-Identical Twins?
Semi-Identical twins, also known as sesquizygotic twins, occur when a single egg is fertilized by two sperm. This results in three sets of chromosomes instead of the usual two. This means that semi-identical twins are genetically similar, but not identical. Semi-Identical twins were first discovered in 2007, and there have only been a few reported cases since then.

When it comes to twins, there’s a lot of confusion about the different types and what they mean. From identical to fraternal, conjoined, and even “half-identical” twins, there are so many variations that it can be hard to keep up.
Twins are fascinating — not just because they share the same womb, but also because of how unique each set is. Whether you’re expecting twins or simply curious about them, understanding the different types of twins can help you better appreciate their special bond and their unique needs or challenges. Our goal in this little corner of the internet is to help parents prepare for navigating the joys and difficulties that come with raising multiples.